In the realm of online security, the terms HTTP, HTTPS, SSL certificates, and SSL encryption play crucial roles in safeguarding sensitive information exchanged between users and websites. With the rapid evolution of cyber threats, understanding these concepts is essential for both internet users and website owners. This blog aims to elucidate the significance of HTTPS, SSL certificates, and encryption in ensuring a secure online experience.
In today’s digital age, where the internet serves as a hub for communication, commerce, and entertainment, ensuring online security has become paramount. As cyber threats continue to evolve, understanding the intricate mechanisms that safeguard sensitive information exchanged between users and websites is imperative. This comprehensive guide aims to delve deeper into the realms of HTTP, HTTPS, SSL certificates, and encryption, elucidating their roles in fortifying online security.
HTTP vs. HTTPS:
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are protocols used for transmitting data over the internet. The key difference lies in the added layer of security HTTPS provides through encryption.
HTTP operates on port 80 and transfers data in plain text format, making it susceptible to interception and tampering by malicious entities. On the other hand, HTTPS employs SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) encryption to secure the data transmitted between the user’s browser and the website’s server.
At the foundation of web communication lies the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), a protocol facilitating the exchange of data between a web server and a user’s browser. Historically, HTTP has been instrumental in powering the World Wide Web, enabling seamless access to information. However, its inherent vulnerability lies in the transmission of data in plain text format, making it susceptible to interception and manipulation by malicious actors.
In response to growing security concerns, the Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) emerged as a fortified iteration of HTTP, integrating encryption protocols to safeguard data transmission. The primary distinction between HTTP and HTTPS lies in the added layer of security HTTPS provides through the implementation of SSL/TLS encryption.
Online Security:
The transition from HTTP to HTTPS is pivotal for enhancing online security. When users access a website over HTTPS, their data is encrypted before transmission, making it unreadable to anyone attempting to intercept it. This encryption ensures the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information such as login credentials, personal details, and financial data.
Moreover, HTTPS offers authentication, verifying that users are communicating with the intended website and not a fraudulent one. This mitigates the risk of phishing attacks and impersonation, bolstering user trust and confidence in the online platform.
SSL Certificates:
SSL certificates are digital certificates issued by Certificate Authorities (CAs) to validate the authenticity and ownership of a website. These certificates contain cryptographic keys that facilitate secure communication between the user’s browser and the web server.
When a user accesses a website over HTTPS, the SSL certificate is presented, allowing the browser to verify the website’s identity. This verification process assures users that they are interacting with a legitimate website and not a malicious imposter.
SSL certificates come in various types, including Domain Validated (DV), Organization Validated (OV), and Extended Validation (EV), each offering different levels of validation and trust. Website owners must obtain and install SSL certificates to enable HTTPS and establish a secure connection with their visitors.
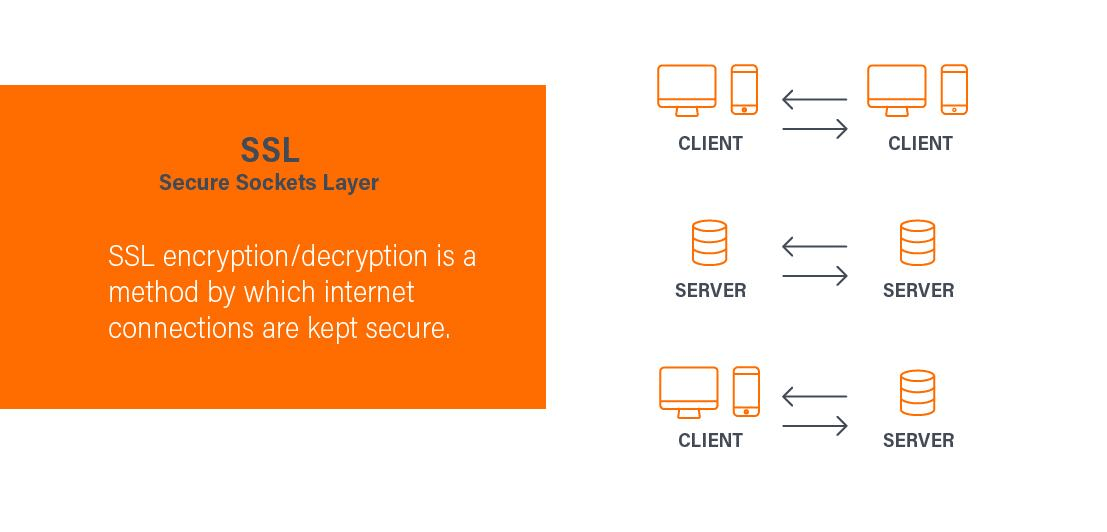
SSL Encryption:
SSL encryption is the cornerstone of HTTPS, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted over the internet. It employs cryptographic algorithms to encrypt plaintext data into ciphertext, rendering it indecipherable to unauthorized parties.
During an HTTPS connection, SSL encryption protects sensitive information from eavesdropping and interception by encrypting it before transmission. Only authorized parties possessing the corresponding decryption keys can decipher the encrypted data, maintaining its secrecy and integrity throughout the transmission process.
In conclusion, the adoption of HTTPS, SSL certificates, and encryption is paramount in safeguarding online security and protecting sensitive data from cyber threats. By encrypting data in transit and verifying the authenticity of websites, these technologies foster trust, privacy, and reliability in the digital landscape. Website owners should prioritize implementing HTTPS and obtaining SSL certificates to fortify their platforms against malicious activities, thereby ensuring a secure and seamless online experience for users.
Also Read : OpenAI Forecasted to Achieve $1 Trillion Valuation, Predicts Former Google China President
Follow On Twitter: Krishna Sahu





Be First to Comment